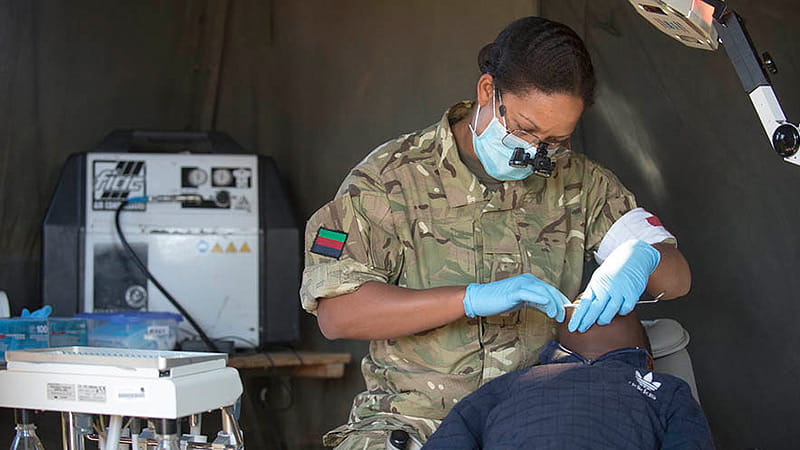
AN army marches on its stomach, Napoleon once said, but toothache, it could be argued, runs a close second to shortage of food when it comes to slowing down a soldier on the way to the battlefield. The old adage being: "an army that cannot bite, cannot fight".
The Army Dental Corp of the British Army was formed in 1921 after World War One with the recognition of the serious wastage of fit soldiers due to the lack of proper dental care – though some historians claim the pivotal moment was when General Douglas Haig was said to have developed a severe toothache around the time of the First Battle of Ypres. Finding that there was no dentist available in the British Army to offer treatment, a French dentist had to be summoned from Paris.
It was later granted the Royal prefix in 1946 and the Royal Army Dental Corp (RADC) today is responsible for the maintenance of dental health among personnel serving throughout the world.
Joining the RADC was an obvious choice for Orianne Moxon, now a major in the service. "When I was doing my A levels, an RADC careers officer came to do a talk for an assembly at my school. I had always had an underlying interest in the Armed Forces and was considering a Gap Year Commission but at that stage I already knew that I was going to apply for dental school. Finding out that I could be a full-time dentist in the Army was a no-brainer for me."
Instead of the Gap Year Commission, which would have seen her get some army training before going to university, Orianne decided to start her dental degree at Bristol University in 2003 first and then make her move. "I applied for a dental cadetship with the RADC when I was in my second year of dental school, and two weeks after my graduation I walked into the arms of the RADC, ready to prepare for the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst a few weeks after that."
Soldier in the chair
Orianne is now one of a 900-strong team employed under the tri-service (Army, Air Force, Navy) umbrella of the Defence Dental Services, which looks after around 200,000 military patients. Her current part in that huge effort is running a single-chair practice in Woodbridge in Suffolk where she is a senior dental officer with the 23 Parachute Engineer Regiment.
So is there a difference between treating soldiers and civilians? "The general dental health needs of the Armed Forces are not too different from the general UK population,” says Orianne, going on to stress some advantages offered by a more protected environment.
"When talking to my civilian colleagues I do feel we are privileged to have a little more time to spend acclimatising nervous patients to treatment without having to worry about the personal financial implications. We do have primary and secondary healthcare referral systems in place, but I think if you can turn a nervous patient around in the primary care dental setting, in the long run you’ve saved a lot of time and money for all."
One of the issues Army dentists do have to deal with, she says, arises because soldiers on operations or exercise are not allowed to drink alcohol. Understandably, they have to seek little pleasures in other ways. "A hard part of the job is trying to administer oral health advice to patients who know full well the oral and general health risks of their sugar and tobacco intake, for instance, but are just not in a position to make any changes. Their cigarettes, sweets or high-energy drink may just be something that helps them get through the long hours, provides some morale and helps them cope with the stress of the day. That is hard to overcome, both as a patient and as their dentist."
Another issue has to do with the hierarchical nature of the services – enlisted men and women are used to taking orders from their superiors. "Gaining informed consent can be interesting too,” she says. “A lot of patients with complicated treatment plans often tell you to ‘Just do whatever you feel is best Ma’am – you’re the boss’."
Even if the dental health needs of your military patient are not that different from those of the average patient on civvy street, the opportunities that arise for a dental officer are another matter altogether. What Orianne has enjoyed most about the job so far, she says, is "the opportunity for personal development – be that through sport, travel, adventurous training, going on exercise or working in and amongst some really interesting military units".
Hearts and minds
Travel has been central to that. From the very start of her training, Orianne has been on the move. After Sandhurst she went to Bulford in Wiltshire to complete her vocational training. She was then posted to Germany for just over three years. “It was a large multinational HQ and there were British, French, Americans, Germans, Dutch, Cypriots and Belgian Armed Forces working there – it was an awesome experience.” Her three years in Germany came with the added bonus of a chance to work in Holland and Belgium, as well as doing some travelling around Europe.
But by far her most interesting and challenging post to date, she says, is the one she completed before starting her current job in Suffolk. "I ran a single chair dental centre on Thorney Island with 12, 16 and 47 Regt Royal Artillery Regiments, whilst also providing the dental care for 33 Field Hospital, who are based in Gosport."
33 Field Hospital’s role is to deliver and provide deployed hospital care in any environment, and the unit has recently completed operations in both Iraq and Afghanistan. So far Orianne has not been deployed on a military operation, but the association with 33 Field Hospital did bring with it the opportunity to take part in Exercise ASKARI Serpent, a training exercise to east Africa which she describes as "the best experience I’ve had so far in the Army".
"I got to lead two dental teams on an exercise to Kenya. We spent four weeks on a hearts and minds medical exercise, visiting remote rural villages and setting up a mobile (tented) primary healthcare unit. We delivered much-needed free healthcare to hundreds of locals alongside a team of regular and reservist doctors, nurses, midwives, health visitors and other allied healthcare professionals, such as paramedics, pharmacists and combat medical technicians."
Going out on the exercise, Orianne had no idea what issues they were going to come up against. One of the first was language, a hurdle crossed with the help of the Kenyan Red Cross, who provided the team with translators. Another was the fact that many of the patients she came across had never actually used a toothbrush. "They do, however, use twigs which although not ideal is all they have."
It was a very different experience to working in the UK but she relished the challenge. "I treated over 200 patients in the space of eight working days, and extracted more teeth than I care to remember. But I will never forget a young warrior called 'Military', aged between 13 and 16, who walked over two hours in the blistering heat, through the bush on his own, to come and see us – we saw elephants walking free across the very same roads he had walked not 24 hours later!”
Go for it
By Orianne’s own admission she had always thought the Army might be the place for her, and her seven years so far have been packed with interesting experiences both inside and outside dentistry. She has no regrets about her decision to "walk into the arms of the RADC" and passionately encourages trainee dentists thinking about a similar career not to hesitate.
"Go for it!" is her advice. “There are opportunities with both the regulars and the reserves, but do your research as to what suits you. The career options aren’t just for new dentists either – qualified dentists, including dentists with specialist interests and beyond, can apply to join the RADC too.
"Oh, and make sure you can run a mile and a half in under 10.5 minutes, and get practising the sit-ups and press-ups!"
Adam Campbell is a freelance journalist and regular contributor to MDDUS publications
This page was correct at the time of publication. Any guidance is intended as general guidance for members only. If you are a member and need specific advice relating to your own circumstances, please contact one of our advisers.
Read more from this issue of Insight Primary
Save this article
Save this article to a list of favourite articles which members can access in their account.
Save to library

